Who is it standing in Berlin Alexanderplatz, very slowly moving from leg to leg? It’s Franz Biberkopf. What has he done? Well, you know all that. A pimp, a hardened criminal, a poor fool, he’s been beaten, and he’s in for it now. That cursed fist that beat him. That terrible fist that gripped him. The other fists that hammered at him, but he escaped.
A blow fell and the red wound gaped.
But it healed one day.
Franz didn’t change and went on his way.
Now the fist keeps up the fight,
it is terrible in its might,
it ravages him body and soul,
Franz advances with timid steps, he has learned his role:
my life no longer belongs to me, I don’t know what to set about.
Franz Biberkopf is down and out.
(Berlin Alexanderplatz, Penguin paperback edition, page 418)
Alfred Döblin
Bruno Alfred Döblin (1878 to 1957) was a German novelist, essayist, and doctor, best known for his novel Berlin Alexanderplatz (1929). A prolific writer whose œuvre spans more than half a century and a wide variety of literary movements and styles, Döblin is one of the most important figures of German literary modernism. His complete works comprise over a dozen novels ranging in genre from historical novels to science fiction to novels about the modern metropolis, several dramas, radio plays, and screenplays, a true crime story, a travel account, two book-length philosophical treatises, scores of essays on politics, religion, art, and society, and numerous letters. (Wikipedia)
Berlin Alexanderplatz’s ‘modernist’ aspects
Berlin Alexanderplatz is not only considered Döblin’s masterpiece but a central achievement of German Modernism. It is often compared to James Joyce’s Ulysses because it, also, is:
– long (478 densely printed pages in the Penguin paperback edition I own)
– urban (not just set in Berlin, but rejoicing in the hectic urban bustle of trams and railway stations, and pubs and bars and music halls and tenements, in 1928 Berlin had a population of four million, p.198)
– concerns ordinary people (The ‘hero’ of Ulysses is Leopold Bloom, a hard-up seller of newspaper advertising space, and Joyce’s novel takes place in just one day, following him as he traipses round Dublin, hustling for work, popping into bars or the public library, attending a funeral and going shopping; the hero of Alexanderplatz, Franz Biberkopf, is distinctly lower down on the social scale from Bloom; he is an uneducated huckster, fresh out of prison, and the novel is set not on one day but much more conventionally, over quite a few months. But, just as in Joyce, we follow the hero around the noisy bustling streets of a ‘modern’ city, seeing adverts and shop windows, overhearing popular tunes and drinking songs)
The most obvious similarity is the shared use of modernist techniques like montage, multi-textuality and stream of consciousness.
Multi-textuality or Tatsachenphantasie
The narrative often switches, casually and with no warning, from third-person storytelling to direct quotation of texts such as newspaper adverts, magazine articles, anatomical textbooks, tram timetables, legal documents, an official breakdown of causes of mortality in Berlin 1928 and so on.
This approach was so novel at the time that it was given a name, Tatsachenphantasie. To quote the Wikipedia article about Döblin’s technique:
His writing is characterized by an innovative use of montage and perspectival play, as well as what he dubbed in 1913 a ‘fantasy of fact’ (Tatsachenphantasie) – an interdisciplinary poetics that draws on modern discourses ranging from the psychiatric to the anthropological to the theological, in order to ‘register and articulate sensory experience and to open up his prose to new areas of knowledge’.
This it certainly does, and I found many of the interpolated documents more interesting – certainly more comprehensible – than the main plot.
Montage
At a slightly higher ‘level’, the narrative is ‘bitty’: it often cuts and jumps to completely different scenes or points of view, sometimes in the one paragraph – directly copying the cutting between shots, between shot sizes and different angles which is the basic technique of movies.
Headlines
An obvious example of this multitextuality is the way the text is broken up by headings which are in the style of newspaper headlines, such as ‘LINA STICKS IT TO THE NANCY BOYS’ or ‘VICTORY ALL ALONG THE LINE! FRANZ BIBERKOPF BUYS A VEAL CUTLET’.
This is easy to understand and can be fun and is not really as modern as it first appears; after all, most novels up to the late 19th century included chapter headings which rambled on at length about their contents. Think of Charles Dickens; as a random example, chapter 14 of The Pickwick Papers is described as ‘Comprising a brief Description of the Company at the Peacock assembled; and a Tale told by a Bagman’, and all the other chapters in this and all his other early novels are given similarly extensive introductory descriptions.
So using newspaper headlines to summarise key events in the narrative can be thought of, and easily assimilated, as an early 20th century variation on a time-honoured tactic.
Stream of consciousness
Almost continually the narrative of events is interspersed with Franz’s memories of prison, fragments of songs, or short phrases running through his head.
In fact, as the novel progresses, this applies to almost all the other characters as well. We are introduced to them by a third-person narrator, then suddenly gets sentences starting with an ‘I’ and realise we have dropped inside their heads to see things from their point of view. The next sentence might be a quote from a song (we know this because it rhymes). The next sentence is the strapline for an advert ‘I’d walk a mile for Mampe’s brandy, It makes you feel like Jack-a-dandy’ (p.33). The next sentence mashes together ‘thoughts’ the characters had in an earlier scene – the whole thing recombined to depict the way thoughts purl and slide around inside our minds.
So there can be passages, paragraphs, made up of elements like the above, the interesting thing is how quickly you get used to it, and to read it. Occasionally a lot of quick cuts are confusing, but not often. So far, so similar with Joyce, then.
Joyce versus Döblin
But I’d say Berlin Alexanderplatz differs from Ulysses in one big respect: in the basic attitude to prose.
Joyce was not just a great writer, he was a writer of genius with a Shakespearian ability to command the English (and other languages) to perform almost any trick he wanted. All his works go beyond brilliant experiments in style and diction, beyond amazingly accurate parodies and pastiches, to actively dismantle the English language altogether.
Take the opening pages of Portrait of the Artist As A Young Man, which use baby talk to try to capture the infant thought processes of a baby which can barely speak; or almost any passage once you get into the main body of Ulysses.
What most characterises Ulysses is less the ‘mechanical’ and obvious aspects of modernism listed above (collage, stream of consciousness) but Joyce’s crafting of different prose styles to reflect each of the chapters and episodes in his story, each successive chapter becoming harder to read as it accumulates verbal references to previous events, given in evermore fragmentary form, and as the English language itself starts to break down as words merge and recombine, leading up to the delirious scene in the brothel where not only the characters, but the English language itself gets totally trolleyed and explodes.
As Ulysses progresses, it becomes more involved in a huge range of verbal special effects designed to convey the mood of, say, a Dublin pub full of heavy drinkers, the section in a library in which Joyce performs a tour de force describing the scene in language which mimics the evolution of the English language from its roots in Anglo-Saxon right through each century’s changing styles up to the present day.
At the novel’s climax, language breaks down completely as it mimics a host of drunken minds caught up in a drunken riot in a brothel. Then Ulysses concludes with the famous final chapter which consists of one vast flowing stream-of-consciousness rendition of the thoughts of a dozing woman (Molly Bloom, Leopold’s wife).
There is nothing at all like this level of verbal ambition in Berlin Alexanderplatz. On the contrary, long stretches of the prose – at least in the 1931 translation by Eugene Jolas which I read – is surprisingly flat, colourless and factual.
Thus Franz Biberkopf, the concrete-worker, and later furniture-mover, that rough, uncouth man of repulsive aspect, returned to Berlin and to the street, the man at whose head a pretty girl from a locksmith’s family had thrown herself, a girl whom he had made into a whore, and at last mortally injured in a scuffle. He has sworn to all the world and to himself to remain respectable. And as long as he had money, he remained respectable. Later, however, his money gave out: and that was the moment he had been waiting for, to show everybody, once and for all, what a real man is like. (p.42, last words of Book One)
See what I mean? The prose, in and of itself, often holds little or no interest. It is routinely as flat and grey as old concrete.
One effect of this prose flatness is to make the multi-textuality, the montage and the modest fragments of stream-of-consciousness much easier to recognise and to assimilate whenever they appear. The transitions may be abrupt, but the prose of each fragment is always complete and definite.
That crook Lüders, the woman’s letter, I’ll land you a knife in the guts. OLORDOLORD, say, leave that alone, we’ll take care of ourselves, you rotters, we won’t do anybody in, we’ve already done time in Tegel. Let’s see: bespoke tailoring, gents’ furnishings, that first, then in the second place, mounting rims on carriage wheels, automobile accessories, important, too, for quick riding, but not too fast. (p.135)
A little tricky, but from the context the reader knows that this a description of Franz walking through the streets of Berlin, his eyes registering advertising hoardings and shop frontages (bespoke tailoring, automobile accessories), angrily thinking how the crook Lüders betrayed him (which he knows from the letter she sent him) and in Franz’s violent fantasy he imagines stabbing him in the guts, but then contradicts this thought using ‘we’ to refer to himself, trying to quell his appetite for violent revenge by telling himself that ‘we’ (i.e. he, Franz) are not about to ‘do anybody in’, because ‘we’ have already ‘done time’ in Tegel, the name of the prison where he was locked up.
And – another crucial difference with Joyce – even if some passages like this take a bit of effort (though not much) the prose, sooner or later, returns to normal. We return to fairly flat, factual prose and know where we are again.
So Alexanderplatz is a bit confusing, yes, but not impenetrable as a lot of Ulysses quickly becomes (without repeated study). Compared to Joyce’s extraordinary and extended experiments with English prose, reading Berlin Alexanderplatz doesn’t present any real verbal challenge.
By far the hardest thing about reading this book, I found, was nothing to do with its (fairly tame) modernist techniques: it was trying to figure out why the devil the characters behave as they do. At almost every key crux in the plot I didn’t understand what the characters were doing or why (see plot summary, below). The net effects of reading the book were:
- enjoyable modernist experimentalism (I liked the insertion of newspaper headlines, official documents etc into the text)
- repulsion at the casual lowlife brutalism of almost all the male characters (see below)
- complete inability to understand why the characters behaved as they did (for example, the complex sex/love lives of Franz and Mieze and Eva, described from Book Seven onwards)
Nine books
Berlin Alexanderplatz is divided into nine ‘books’. Each book is prefaced by a couple of paragraphs describing in general terms what will happen in it, another trait reminiscent of English 18th century novels. Indeed, the entire text is preceded by a one-page summary anticipating the shape of the action, a little as a Greek tragedy is introduced by a chorus telling us what is going to happen.
The obvious difference is that these half-page introductions have more the quality of a fable or children’s tale, not least because they generally include deliberately trite jingles or doggerel.
Biberkopf has vowed to become respectable and you have seen how he stayed straight for many a week
but it was only a respite, so to speak.
In the end life finds this going too far,
and trips him up with a wily jar.
To him, Franz Biberkopf, however, this doesn’t seem a very sporting trick,
and, for a considerable time, he finds this sordid, draggle-tailed existence, which contradicts his every good intention, a bit too thick.
(Intro to Book Three, p.105)
This fondness for cheap songs, doggerel poetry, advertising jingles, and sometimes just random rhymes, becomes more noticeable as the book progresses and is every bit as prominent as the more obvious NEWSPAPER HEADLINES, insertion of official documents and so on.
In Switzerland, on Tyrol’s height,
One feels so well by day and night,
In Tyrol the milk comes warm from the cow,
In Switzerland there’s the tall Jungfrau. (p.358)
The children’s fairy tale feel is emphasised by the way that, in the one-page preface to the whole text, we are told Franz will suffer three blows, three after all being the canonical number in fairy tales (little pigs, Goldilocks bears, billy goats gruff etc).
Three times this thing crashes against our man, disturbing his scheme of life. It rushes at him with cheating and fraud. The man is able to get up again, he is firm on his feet. It drives and beats him with foul play. He finds it a bit hard to get up, they almost count him out. Finally it torpedoes him with huge and monstrous savagery. (p.7)
Greek and Bible imagery
Joyce’s Ulysses is (although it’s hard to make this out on a first reading) loosely structured on Homer’s ancient Greek epic poem, The Odyssey, with Leopold Bloom wandering round Dublin rather as Odysseus wanders round the Mediterranean, loosely sought by young Stephen Daedelus, in roughly the way that Odysseus’s son, Telemachus, searches for his father in Homer’s poem – until, at the climax of the book, they are reunited.
Again, Berlin Alexanderplatz doesn’t have anything like the same ambition or scope as the Joyce. Instead it contents itself with occasional references to ancient Greek legends or Bible stories, which pop up as ironic references, sometimes taking up a couple of pages of extended description, and thereafter popping up again as anything from paragraphs interrupting the main narrative, sometimes just one-phrase reminders.
So, for example, the sense that Franz’s story is like a Greek tragedy is made explicit in the numerous references throughout the book to the plot of the ancient Greek Oresteia in which, while King Agamemnon is away at the Trojan War, his wife Queen Clytemnestra has an affair and, upon his return, murders Agamemon in his bath. Whereupon their son Orestes returns and murders his mother and her lover. Whereupon Orestes is pursued everywhere by the Furies who torment murderers. On a number of occasions Franz’s self-torment over his killing of his girlfriend Ida is compared to Orestes and the Furies. It is not, in other words, a very difficult allusion.
Towards the end of the book, as Franz’ tribulations build up, there are some extended (two- or three-page-long passages) which quote the Book of Job from the Bible, explicitly comparing Franz to Job (pp.146-149, 399). Again, fairly obvious.
There’s an extended comparison with Abraham teetering on the brink of sacrificing his son, Isaac (pages 298 to 299). And as we see more of the murderous underworld Franz has got involved in, the text interpolates quite a few references to the Whore of Babylon, quoting descriptions of her from the Bible’s Book of Revelation (pages 266, 306, 400, 446)
The woman is arrayed in purple and scarlet colour and decked with gold and precious stones and pearls, having a golden cup in her hand. She laughs. And upon her forehead is a name written, MYSTERY, BABYLON THE GREAT, THE MOTHER OF HARLOTS AND ABOMINATIONS OF THE EARTH (p.266)
These high literary references sort of enrich the text though, to be honest, I found them a bit boring, less interesting than the newspaper reports Döblin interjects about scandalous murder trials being reported in the newspapers or quotes from communist or Nazi articles or even the extended description of the Berlin slaughterhouses in chapter four (pages 138 to 145). The Oresteia, Job, I know all about; the inside of a Berlin abattoir circa 1928 is a sweaty bloody revelation.
Collapsing house imagery
Also – sewn in among all the other impressions of the city or of Franz’s scattered consciousness – Franz has a recurrent vision of Berlin’s houses collapsing, their roofs sliding off, cascades of tiles sliding off rooftops and crashing down on him.
Repetition makes this recurring metaphor for Franz’s panic attacks acquire a real charge and ominousness.
Collapsing house imagery pages 13, 120, 240, 265, 314, 471.
Plot summary
Book one (pages 11 to 42)
It is 1927 (p.97).
Franz Biberkopf (the surname translates literally as ‘beaver head’) is released from Tegel prison on the outskirts of Berlin. He is 5 feet 10-and-a-half inches tall (p.176).
He has served four years for the manslaughter of his girlfriend, Ida (‘I knocked that tart’s ribs to pieces, that’s why I had to go in jug’, p.34. A detailed anatomical description of their fight, which quotes Newton’s Laws of Thermodynamics, is given on page 98).
Franz had been a cement worker, then a furniture remover, among numerous odd jobs (p.96). He catches a tram into town and wanders, dazed at being a free man, through the hectic streets, terrified of the hustle and bustle.
Terror struck at him as he walked down Rosenthaler Strasse and saw a man and a woman sitting in a little beer shop right at the window: they poured beer down their gullets out of mugs, yes, what about it? They were drinking: they had forks and stuck pieces of meat into their mouths, theyn they pulled the forks out again and they were not bleeding. (p.12)
Crude, isn’t it. In fact it’s almost as crude as language and psychology can get without sinking below the level of human articulation altogether.
Franz retreats into the courtyards of tenements in Dragonerstrasse (p.35), where he is taken in by a couple of Jewish men who (bizarrely) argue fiercely among themselves while they tell him the life story of young Stefan Zannovich the con man who ended up committing suicide in prison, and whose body was taken away by the knacker. It is a strange, offputting start to the book. First time I read it, I gave up at this point.
Having sobered up, as it were, Franz sets off into the streets again, dazed by freedom and the hustle and bustle of the Berlin crowds. A population of four million.
He decides – in the blunt crude German way we got used to in Hermann Broch’s novels – that he needs ‘a woman’ to calm down, but when he picks up and goes home with two successive prostitutes, can’t get an erection with either of them. Cue some multi-textuality when a textbook account of impotence is inserted into the text and, a little later, an advert for an aphrodisiac.
Day three and Fritz finds himself knocking at the door of the sister of the girlfriend he murdered, Minna, who reluctantly lets him in, then he rapes her, rather as August Esch rapes Mother Hentjen in Hermann Broch’s The Anarchist and then Wilhelm Huguenau rapes Mother Hentjen in The Realist.
German rapists, eh, well worth writing novels about. Well, all their wives and girlfriends would be raped to death 16 years later by the invading Russians, so it was good practice.
Finally Fritz feels content, released, free, like a real man again (p.37).
He leaves but comes back in the following days to bring her presents, but Minna rebuffs him every time. She is married and her husband Karl asks her how she got the black eye and bitemarks on her neck, which are the signs of Franz’s assault. Still, they talk quite affably. He comes round with some aprons to replace the ones he tore to shred in the initial rape. She listens, chooses an apron, but is terrified of the neighbours seeing, and keeps crying. The big hearty brute Fritz is quite oblivious to all this.
Book two (pages 45 to 103)
Opens with the characteristic quoting of official texts which read like small announcements from a newspaper, then a detailed technical description of the weather forecast (‘Weather changing, more agreeable, a degree or two below freezing-point’ [which, incidentally, echoes the opening of Robert Musil’s The Man Without Qualities]) and then a list of the main stops of tram number 68, from which Fritz alights amid a blizzard of ad straplines (‘Eat more fish, the healthy slimming dish!’)
It strikes me this is collage: ‘A collage is a composition of materials and objects pasted over a surface.’ The quoted texts may or may not be related, but in a way their unrelatedness demonstrates quite well the classic modernist impulse to embody or describe the chaotic, overwhelming sensory and mental stimulation of the ‘modern’ city.
And so the main action, if you can call it that, is surrounded by side actions, snippets and vignettes of life in the big city. A couple of old geezers chatting in a billiard hall about one of them losing his job. A young woman gets off a tram, is met by her older lover, who takes her to the flat of a friend, while she worries all the way about what mummy and daddy would say if they found out.
It is a few weeks later and Franz has found somewhere to live, has raised some money from savings and selling off furniture, and so is smartly dressed and going round with a plump new Polish girlfriend, Lina, Lina Przyballa of Czernowitz, the only legitimate daughter of the farmer Stanlislaus Przyballa (p.74), according to Lüders, a ‘little fat thing’ (p.118).
They come across a newspaper seller located in a doorway and – this is very obscurely described – he appears to also sell illicit gay magazines and persuades Franz to take some. Franz presents them to Lina in a café but she is disgusted and insists they go back to the shabby old seller and Franz watches from across the road as she yells at the seller then throws the magazines on the floor.
It is typical of the book’s technique that this ‘story’ is interrupted by an imaginary vignette of a respectably married old chap (a ‘greypate’) who one day picks up a pretty boy in the park and calls him his sunshine and takes him to a hotel room. It’s not even suggested that they have sex, but the hotel room has peepholes and the owner and his wife spy on the pair and then report them to the police. He is hauled up in court but persuades the judge nothing happened; but a letter detailing his court appearance and aquittal is posted to his home where, away on business, his wife opens it and the poor man returns home to weeping and lamentation from his wife (pp.72-3)
Meanwhile, Franz rejoices over his girlfriend’s victory over the magazine seller by forking her on the sofa, then they stroll along to the Neue Welt pub in the Hasenheide Park – musicians in Tyrolese costume, beer drinking songs – ‘Shun all trouble and shun all pain, Then life’s a happy refrain’ (p.76) a Charlie Chaplin impersonator on stage, you can buy tickling sticks. Döblin, like a camera, roams among the crowd, alighting briefly on the second fitter of an engineering firm in Neuköln, two couples necking, soldiers with their floozies, there’s weight-lifting competitions and see-your-future-wife stalls. Franz gets plastered and ends up at the bar with a fellow drunk complaining about having fought the French, being a patriotic German, but no job, down on his luck, he’s going to join the Reds.
It’s a deliberately whirligig chaotic depiction of a set of connected, loud, smoky, drunken music halls, yet it’s worth noting that the prose never ceases to be correct. It’s just broken up into short sentences, with frequent quotes from the cheap songs. But the sentences themselves don’t collapse, neither do the word themselves break up and intermingle, as they do in Joyce.
Franz now peddles Nordic Nationalist papers. He’s not against the Jews but he’s for law and order. The narrative immediately includes block quotes from said Nationalist papers, well conveying the wheedling tone of aggrieved Fascist propaganda. Franz is down the pub with mates, some of whom reminisce about their service in the war, then the trouble afterwards i.e. the communist uprisings in Berlin and elsewhere. Then the inflation and the hunger.
Franz’s drinking buddies (Georgie Dreske and Richard Werner, the unemployed locksmith, p.80) down at Henschke’s bar take exception to the Fascist armband Franz has taken to wearing. They argue about their war records.
Next night, when Fritz goes there, there are a few strangers with his mates, they all look at him surlily, the sing the Internationale. Franz recites a poem written by a fellow inmate, Drohms, then overcome with sentiment goes on to sing The Watch On The Rhine. This doesn’t stop one of the new boys starting a fight, a table is overturned, a plate and glass smashed, but then they back off and Franz walks out to bump into Lina who’d come to meet him there. She shows him a Peace newspaper with a sweet poem about love. She snuggles up to him and quietly suggests it’s time they got engaged.
Franz is prone to bad dreams, pangs of conscience. It is partly to quell this psychological eruptions that he longs for Order and Discipline which means escape from his personal demons. This leads to an extended passage about the fate of Agamemnon home from the Trojan War who is murdered by his wife Clyemnestra, who is then murdered by her son Orestes, who is pursued by the Furies – as Franz is by his bad dreams. The section includes a clinical description of how Franz murdered his wife – in fact, in the heat of a row, he hit her twice in the guts with a whisk, but the blows were enough to break a few ribs, rupture a lung, prompt several infections from which she died miserably in hospital five weeks later. And a characteristically ironic modernist juxtaposition of the hilltop flares which signalled the arrival of Agamemon home, with a technical description of the activity of modern radio waves.
Book three (pages 107 to 121)
In this fairly short book, Franz is embroiled with Otto Lüders, a more than usually disreputable prole who’s been out of work for a couple of years (a factual interlude in the previous book detailed the rise in unemployment at the end of 1927). Franz is now selling bootlaces on the street or hawking them door to door. He arrives in the pub for a drink with Otto and swankily tells him he’s made 10 marks (apparently a tidy sum) out of a woman, a skinny widow women who invited him in for a cup of coffee and he left his whole stock there. I wasn’t sure, but I think the implication is that Franz gave her one, as the saying goes. He also seems to have left his entire stock there, though whether as a gift or an oversight I couldn’t work out.
Anyway, next day Lüders sneaks along to the building, finds the same widow woman, forces his way in under pretence of being a door to door salesman, extorts a coffee out of her and terrifies her so much, he is able to nick a whole load of stuff, her table cover, sofa cushions etc, and legs it.
With the result that, next day when Franz goes round to see her with a bouquet of flowers, the widow woman slams her door in his face. Franz tries a few times more then leaves her a note telling her to bring his stuff to a pub. But she doesn’t. Otto enters said pub, spots Franz looking hacked off, turns and legs it. Franz puts two and two together.
Interlude of a war veteran whose four-year-old son has just died because the doctor was too busy to come and see him. He’s loitering outside their apartment house then goes to see the doctor to give him a piece of his mind, then goes upstairs to where his wife is weeping.
Franz is so distraught at Otto’s betrayal that he ups and leaves. Pays off his landlady, packs his things and leaves his flat. Doesn’t even tell Lina. Lina asks their friend (‘little’) Gottlieb Meck to find him. Meck goes for a beer with Lüders and then, in one of those scenes I find so disconcerting about this German fiction, walking down a dark street pounces on him, knocks him to the floor, beats the crap out of him and threatens him with a knife, telling him to locate Franz.
Next day Lüders reports back. He’s found Franz in a boarding house just three numbers down from his former place. Like Meck, Lüders keeps his hands on an open knife in his pocket as he goes into Franz’s room, finds him on the bed with his boots on, depressed. Frane yells at him to get out, then throws the bowl of washing water at him, Lüders insists he’s not right in the head.
Book four (pages 125 to 167)
It is February 1928 (p.151)
Lengthy description of all the inhabitants of the tenement in Linienstrasse which Franz has moved to, with intertextuality e.g. the description of lawyer Herr Löwenhund is interrupted by direct quotes from legal documents he’s dealing with or letters he’s written. Tatsachenphantasie.
Franz is lying around in the squalid room he’s renting, drinking all day. I still can’t figure out why Lüders going behind his back to threaten the skinny widow woman has affected him like this.
A lengthy description of the abattoir and slaughterhouse district of North Berlin, giving facts and figures as in a government report, then moving on to a precise and stomach-churning description of precisely how they slaughtered pigs and cattle.
With a weird interlude about the story of Job from the Bible.
Which then goes on to an extended yarn about the caretaker of a warehouse, a Herr Gerner, who is persuaded to fall in with a bunch of burglars who want to break into it, to the extent that after the break-in he allows them to stash all the stolen goods in his house. In some obscure way which is hedged around, I think he allows his wife to sleep with the youngest, tallest and handsomest of the thieves. I think. I couldn’t make it out. Anyway, the next morning the police call round and arrest him. Franz saw some of this happening i.e. an initial attempt of the burglars to climb over the wall and pinch some stuff, but he refuses to squeal to the cops.
It is freezing cold February morning and on a whim, Franz decides to go and visit Minna who he hasn’t seen for a while. But the door is opened by Minna’s husband, Karl, who sends him packing with a flea in his ear.
Book five (pages 171 to 223)
A very enjoyable panoramic overview of Alexanderplatz with its roadworks, shops, trams and hustling crowds. It is the evening of 9 February 1928, and little Meck bumps into Franz selling newspapers again. They go to a bar and have inconsequential chat with other working class men. All the antagonism Franz prompted by selling nationalist papers and wearing a swastika armband seems to have disappeared.
Franz gets into a some kind of ‘scheme’ with a slim stuttering man who wears a shabby army greatcoat named Reinhold (‘that quite insignificant figure, a mouse-grey lad in mouse-grey’, p.203). This Reinhold is a serial womaniser and takes a new girlfriend each month and shifts his previous one onto Franz. I really didn’t understand what anybody has to gain from this or why they’d do it, but a certain Fränzl comes to be Franz’s grilfriend for a month or so, and then she’s replaced by silly Cilly, and I think Franz then passes them onto little Ede the hunchback. I think that’s what happens.
As I mentioned above, I find the passages where the character’s walking through the streets, and the text cuts from his thoughts to advertising straplines, song jingles, a Berlin tram timetable, a leader from that day’s newspaper – the familiar technique and content of ‘modernist’ literature – easy to understand and enjoyable to read. In fact the passages where Döblin just inserts highlights and stories from the day’s newspaper are interesting social history.
But I find many passages of the apparent plot inexplicable: how exactly did the thieves persuade the nightwatchman Gerner to join them and what went on between the handsome one and Gerner’s wife? Why did Lüders going round to see the skinny widow woman upset Franz so much that he dumped Lina and moved apartment? What had Lina done wrong?
The modernism stuff is easy-peasy to process and, as the book progressed, I enjoyed the cumulative collage of Berlin life circa 1928 which it built up. Whereas the bones of the plot – what the characters were doing and why – I frequently found incomprehensible.
Franz gets fed up of getting Reinhold’s hand-me-downs every month. Cilly puts up a fight and Franz decides to stick with her and tells Reinhold, who storms off in a huff. Characteristically, that night Reinhold dreams of murdering his current squeeze, Trude.
Disaster strikes
It is the second week of April 1928. Easter. Franz pops out from his 4th floor apartment, leaving Cilly. It’s snowing. He bumps into an asthmatic man who tells him about a scam he carries out, which is to offer to buy old junk off people, he turns up, removes the junk, then slips a mimeographed card through their doors saying that ‘due to unforeseen circumstances’ he can’t pay, and legs it, Franz thinks he’s a bit bonkers.
They come across a brawl, a crowd has gathered round it. Franz pushes to the front and is enjoying the fight when he realises one of the fighters is Emil, a mate of Reinhold’s he’s seen around. Just then the cops arrive to break up the fight and Franz charitably helps Emil away to shelter in a doorway.
Here Emil tells Franz he’s going to stagger home – he got fairly beaten in the fight – but asks Franz to do him a favour: can he pop round and tell a man named Pums (who we’ve met knocking about the bars) that he, Emil, won’t be able to help with a spot of removal they’re planning to do. Franz pleads that he ought to go home & see Cilly, but Emil persuades him to go and see Pums, the house is just nearby. So he does. And Pums offers Franz money to help out with the removal, say five marks an hour for a few hours.
Franz is still reluctant and wants to go tell Cilly where he is, but Pums says there’s no time, they’ll be leaving soon, they give Franz a pen and paper and he scribbles a note to Cilly saying he’s unexpectedly on a little job. Pums’s girlfriend takes it – takes it next door and burns it in the fire…
To cut a long grim story short, Franz is piled into one of two cars with Pums and a few other guys including Reinhold, who we discover is one of ‘Pums’s men’. They drive for a long time to the outskirts of Berlin. And here he suddenly finds himself tasked with acting as lookout while the men comprehensively loot a warehouse, filling the cars with booty. Franz is basically an honest man and gets cold feet, makes to protest but Reinhold hits him very hard on the arm, while the men shuttle past him in the dark, their arms full of loot. Franz makes a second bid to leave, but they’ve finished anyway and drag him into the car, as both accelerate off.
But they see that someone’s spotted them and another car is in pursuit. Then something strange happens in the second of the two escaping crim cars. When Franz hears that another car is in pursuit, Franz stupidly grins. He was very anxious about being the lookout and resented being hit and threatened by the others and now, like an idiot, grins. Reinhold, squashed in next to him, asks him why he’s grinning, the damn idiot and then Reinhold’s resentment at Franz bubbles up. I found this – as I found all the motivation and psychology in the book – hard to understand, but it seems that although Reinhold persuaded Franz to join his scheme of taking his cast-off women, now – obscurely – in the stress of this tense moment – he resents it, comes to think Franz exploited him somehow, knows dangerous things about him. Franz’s idiotic grinning in the flickering light of the streetlamps which whizz by triggers a sudden surge of hatred in Reinhold and…
Reinhold signals to one of the other guys to fling the car door open… someone punches Franz in the face… Reinhold pushes Franz away from him and over the pile of stolen goods… Franz slips out the car but clinging onto the running board but the others hit him on the arm and thigh and then a crashing blow on the head.
Franz falls into the road and the car following close behind runs over him.
Book six (pages 227 to 315)
Is Franz dead? The narrative cuts to Reinhold the next day, drunk as a skunk before noon, his girlfriend, Trude, who he’s tired off, whines a little, so he beats her face to a pulp, smashing up her mouth and ruining her looks for ever, she runs away taking her stuff. Still drunk, Reinhold swanks around, remembering the job they did last night and feeling mighty proud of himself.
Poor Cilly waiting in his apartment for him to return, then going out into the snowy streets to find him. She bumps into Reinhold dressed up to the nines and very confident. She had brought a kitchen knife with her to tab him with (!). He doesn’t know this, but blames everything on Franz, says Franz has run off with Reinhold’s last girl, Trude, and promises Cilly they’ll get back together soon, and somehow casts his magic over her so she goes off mooning over him.
Now we learn that some other motorists find Franz in the road, load him into their car. Half conscious he asks to be driven to a bar in Elsasser Strasse and request an old friend of his, Herbert Wischow. Herbert is found and he and his girlfriend Eva taken Franz to their flat and change and dress him. Only then do they drive him to a private hospital in Magdeberg.
Why? I don’t know. This, as so much of the actual plot, seems incomprehensible to me. Why didn’t Franz just ask to be rushed to the nearest hospital?
In the hospital at Magdeburg the doctors amputate his right arm (!) and fix other broken bones. Then Wischow and Eva take Franz home to recuperate with them. Old friends from before Tegel drop by. Wischow is upset because Franz didn’t come to see them when he got out of prison and, now, that he’s gotten involved with a crook like Pums. Slowly it comes out that Franz didn’t want to go on the job, didn’t know what they were up to, is a victim in every way. Wischow asks questions about Pums and the gang and spreads the word about how they ill-treated Franz. The mood of the underworld turns against Pums’s mob. Some of them suggest having a whip round to give Franz compensation, and they raise several hundred marks but when Schreiber goes round to deliver it and puts his hand in his pocket, Eva has a hysterical fit thinking he’s going to pull a gun and shoot Franz, Franz staggers back, chairs fall over, panic, Schreiber runs off down the stairs, later claiming he gave the money to Eva, and which he keeps for himself.
It’s June 1928 (p.246). Franz determines 1. not to squeal 2. to live independently. He goes to the Charity Commission, he gets a job calling out circus attractions. He bumps into his buddy Meck and, realising the Pums gang have told him one story, tells him a far more heroic version where he, Franz, fired a gun at detectives stumbling over the burglary and the tecs shot back injuring his arm. The aim is to let the Pums gang know he’s not peaching.
Franz determines to resume normal life, to get a job. He picks up a pretty little thing named Emmi who’s been stood up in a bar. Franz is entertaining, they go to a crowded bar. A man with no legs pushes himself along in a kind of trolley. The younger men say anyone who fought and was injured in the war is a fool. When they ask Franz’s other arm is he says his girlfriend is very possessive, so he left it at home with her as a pledge that he’d come home. Laughter.
Franz buys a smart suit, wears a stolen Cross of Iron, looks like a respectable butcher, uses a set of false papers belonging to one Franz Räcker, which have done the rounds of the criminal world. Herbert & Eva have been away at a spa. She is the part-time fancy woman of a rich banker. He takes her to the spa, dresses her, dines her and ****s her. One evening, just after he’s withdrawn 10,000 marks from the bank, they go down for dinner and it is burgled. The implication is it was stolen by Herbert, her lover, who’s followed the couple out there and is tipped off about the money.
Back they come to Berlin, Eva having to live in the fancy apartment the banker puts her up in, hoping he soon tires of her. She can get away fairly often, and she and Herbert introduce Fritz to a pretty young girl they’ve picked up tarting at the Stettin station. Franz is bowled over by this pretty little thing, fresh as a schoolgirl – initially she’s called Sonia, but Franz prefers to call her Mieze (her real name is in fact Emilie Parsunke, p.269).
Franz becomes a pimp
There’s a hiccup in their relationship when Franz discovers she’s getting letters from admirers. Upset, he goes round to Herbert and Eva’s, Eva pushes Herbert out the door and then falls on Franz, ravishing him. She has been in lust with him for ages and seeing him all upset triggered her off. After they’ve had sex, Eva gets dressed and rushes off to find Mieze. Then returns, all straightened out. Mieze loves Franz but has been meeting during the day with ‘admirers’ and extorting money out of them. Franz is relieved, overcome with love, and hastens off to find Mieze, they return to his flat and are more in love than ever.
See what I mean about being confused by the behaviour of the characters. So Franz can have sex with the wife of one of his best friends, all the time upset about her being unfaithful to him, then the best friend’s wife goes to interpose on his behalf, and when it comes out that Mieze has other male admirers who (I think) she has sex with in order to generate income for Franz, everyone is relieved!
And so, in a way which I once again didn’t understand, Franz acknowledges that he has become a pimp (pp.278, 286, 313). Has he? Alright, if the narrator says so, but I found the events & behaviour of the characters hard to follow and almost impossible to understand.
Eva invites Mieze round to their nice apartment but when she admits that she’d like to have a child by Franz, Miese is overjoyed and kisses her and makes a lesbian pass at her (?)
Mieze soon gets set up with a rich admirer, married, who sets her up in a nice flat, though she carries on adoring Franz. Eva comes round and ravishes Franz again, although he’s in love with little Mieze. What if she gets pregnant, worries Franz. Oh she’d love to, replies Eva.
Franz attends political meetings with a mate, Willy, in fact a lowlife pickpocket but who enjoys getting chatting to politically minded workers at communist or anarchist meetings. Both Eva and Mieze want Franz to stop attending the meetings and/or hanging out with Willy.
Extended passage where an old anarchist explains to a sceptical Franz how the ruling class of every nation exploits the workers, but how a communist regime would just substitute a new exploiting class (pp.281-286). Willy, by contrast, is a devotee of Nietzsche and Stirner, and believes a man should do as he pleases.
August 1928. Mieze is settled into being her married man’s mistress, meanwhile remitting the money to Franz, who is thus living off immoral earnings, while Eva continues to love him. Franz pays a visit to Reinhold, who is terrified he’s going to do something. Franz does noting, goes away, feels restless and so returns to Reinhold’s apartment.
What is incomprehensible to me is Franz’s fatalism, the way he seems to bear no grudge against Reinhold for making him a cripple, he says he knew some kind of change had to happen in his life.
Somehow having confronted Reinhold and got it off his chest makes him happy. That night he dances the night away with Eva, while all the time imagining the two he loves, little Mieze (fair enough) and Reinhold. As I keep saying, it’s difficult to follow or understand the psychology. (Though, to be fair, Herbert and Eva are puzzled as to why Franz keeps going round to see the man who was responsible for him losing his arm, p.325).
Book seven (pages 319 to 372)
Opens with pages devoted to some Tatsachenphantasie with an account of one-time air ace Beese-Arnim who is convicted of murdering his girlfriend. And we are given a list of notable America officials who are visiting the German capital. And brief factual accounts of some of the cases passing through the Labour Law Courts. And then a working class girl Anna posts a letter to her boyfriend suggesting they split up. And a young woman of 26 writes in her diary how miserable and weak her periods make her feel, and how she often wants to kill herself.
August moves into September. Franz has unashamedly joined Pums’s gang. They’re as puzzled as Herbert and Eva but when Franz stands there in front of them saying let bygones be bygones, and they all know he hasn’t snitched to the cops, they have to admit he’s right. So they let him in.
Then we learn some of the challenges of selling on stolen goods. Pums’s fence is playing up. Eventually they carefully plan and pull off a job which requires teamwork, one duo lying low in offices above a place where valuables are kept, waiting till the early hours then drilling down through the ceiling, lowering a rope, while they open the door to this upstairs apartment to let other members get in and pass up the swag, pile it, take it down to the car, clear up after themselves with the smoothest member of the gang, elegant Waldemar Heller, taking a dump on the floor as a calling card (p.335).
Reinhold decides to pay Franz’s woman a visit, when he’s not there. He climbs the stairs to ominous accompaniment by the narrator, and slicks his ways past Mieze at the door, and lolls on her sofa and calmly describes the way he and Franz used to pass on women between each other. I was scared he was going to murder her, why? Because he’s German and this is a German novel, but in fact he just heavily implies that Franz might be considering swapping her – all the time openly eyeing her up, before slipperily seeing himself out. Which leaves Mieze with her heart pounding and her thoughts all mixed up with the lyrics of a sentimental love song being played by an organ grinder outside the house (‘In Heidelberg Town I lost my heart…’)
Anyway, a few days later another peculiar scene unfolds. Knowing Mieze is out, Franz takes Reinhold back to his apartment and hides him in the bedroom. Reinhold has been pestering Franz about Miese, what’s she like, remember when they used to swap girls etc, so Franz hides Reinhold with the intention of showing him what a Lady is like, what a pure good girl is like. But unfortunately Mieze comes in and clings to Franz really closely. She’s been away for a few days with her middle-aged gentleman lover. But now she tearfully confesses to Franz that the man brought his young son, a dashing handsome man who made advances to Mieze and so Franz asks whether she loves him and Mieze makes the bad mistake of saying Yes.
At which point Franz goes mental and I thought was going to batter her to death, he slaps her, beats her to the floor, throws himself on her I thought he was going to crush her, one of her eyes is closed, blood is running from her broken lips. Ironically, this is the night Franz chose to bring a witness home to their love and Reinhold watches in amazement, then tries to pull Franz off the cowering whimpering girl. Franz pulls on his coat and storms out and the girl staggers to the staircase shouting after that she still loves him.
Reinhold hesitates to make sure she’s alright, then stumbles down the stairs and out, wiping the blood from his hands.
It is barely believable that the passage ends a few hours later with Franz back in his apartment and Mieze making up to him, billing and cooing, them both in love, and her besotted more than ever with him, the wife-beater.
OK, I can grant that some women become in thrall to their beating partners. But the next scene is a ball given by the Pums gang which Mieze attends in a ball mask as the guest of Karl the tinsmith, dances with all of them, even Franz who doesn’t recognise her (?really) then allows herself to be driven home in a cab with Karl who heavily seduces her, if not has sex with her, in the back of the cab, for some reason having sex with another member of the gang is not being unfaithful, because she’s doing it for Franz, in order to find out more about the gang and help him.
She goes out with Karl a couple of times (telling Franz she’s with the rich gentleman friend). Then Reinhold gets wind of this liaison and muscles in. On a couple of odd occasions he persuades Karl to let him come along when they go on outings to the Freienwalde and its pretty Kurgarten, they stroll past the bandstand, through the woods, back to a hotel where Mieze stays the night, locking her door, the two men sit on the terrace smoking their cigars. That’s Wednesday 29 August 1928.
On Saturday 1 September, they repeat the experience, Karl making himself scarce while Reinhold goes into seduction mode, chatting sweetly to Mieze, while she is happy to go along with his sweet-talk. In an odd moment he undoes his shirt to show her the tattoo on his chest – an anvil – and harshly grabs her head and tells her to kiss it. She recoils, shouting at him, he’s mussed her hair. Nonetheless they move on. He guides her towards a bowl, a hollow in the grass by the woods. by now it’s dark. This entire sequence is very long, some 20 pages and 11 pages are devoted to just this evening walk, which changes in mood as Reinhold is now aggressive, now sweet, Mieze is frightened, then seduced back to walking hand in hand. But when he manhandles her down into the hollow, she starts screaming and fighting back and – in a horrible scene – he pushes her to the ground, kneels on her spine and strangles her from behind (p.370). Murders her. Buries her body under brush, goes fetches Karl who’s waiting at the car, they return and bury her properly, really deep in the soil, then sand, then scatter underbrush over the tomb. Poor Mieze’s smashed and broken body.
Reinhold gives Karl money to get out of Berlin and lie low for while, and keep his mouth shut.
Book eight (pages 375 to 431)
Mieze’s murder turns out to be the motor for the climax of the book. Franz becomes slowly more distraught as Mieze’s disappearance persists, Eva tries the cheer him up and announces she’s pregnant. Franz doesn’t tell many people because it’s shameful to admit his girl has abandoned him.
Weeks pass. It is early October (p.382) The criminals are restless at Pums’s leadership; they want to steal money, he prefers to steal goods and fence them, but they claim he keeps too much of the money. They pull a job on Stralauer Strasse, breaking into a bandage factory at night where there’s meant to be money in the safe. But Karl the tinsmith burns himself on his acetylene torch, none of the others can use it properly, in frustration and anger they pour petrol over the office and set it on fire but throw the match a bit too early and Pums himself gets burned on h is back. They all blame Karl the tinsmith for the fiasco and Karl grumbles, and also resents the way he was used by Reinhold to bury the dead girl.
Karl meets a wheelwright in a bar and they go in together, with two others, on the burglary of a clothing store in Elsasser Strasse. They get chatting to the nightwatchman, get invited in to share a coffee, then break it to him that they’re going to burgle the place, they’ll tie him up, give him some of the proceeds – although when they have tied him up they amuse themselves by beating him a bit round the face and nearly smothering him with a coat over his head. They are not cartoon thieves, they are thoughtless brutes, almost all the male characters in this book.
Next time the Pums gang invite Karl to join a job he is high and mighty and words are exchanged, between Karl and Reinhold especially. Which makes them suspicious of him. Then Karl and the wheelwright are arrested by the police. Their fingerprints match the ones found all over the clothing store watchman’s office and he identifies them. Karl is convinced that Reinhold snitched on him as revenge for him not joining that last job.
Karl asks a respectable in-law to find a lawyer for him and then runs past the lawyer where he would stand if he reveals he was involved in burying a dead body. The lawyer cautiously asks if he had any part in the body’s death. No. Lawyer leaves. Karl stews all night. Next day, hauled up in front of the judge, he snitches on Reinhold, telling the judge and police in great detail how he helped Reinhold bury the body of the young woman he, Reinhold, had murdered.
Karl leads the police to the burial site, they dig, there’s no body in the hole but some scraps of clothing and the hole has obviously recently been dug up i.e. Reinhold got wind of what was happening and moved it. When police publicise the case two garden labourers (p.395) come forward who saw Reinhold lugging a heavy case to another part of the woods. Digging here, the police finally find Mieze’s corpse.
This narrative – in itself not unlike a basic murder thriller plot – is given a light dusting of ‘modernism’ with the insertion of some Tatsachenphantasie – newspaper reports about a tenement block collapsing in Prague, an ambitious early flight of the new Graf Zeppelin over Berlin, and so on (p.397).
Meanwhile, Reinhold gets wind of all this & tries to diffuse the blame by getting Franz involved. He comes round to tell Franz they’re arresting people for the last Pums gang job, telling him to do a runner. Franz goes into hiding in a villa in Wilmersdorfer Strasse (p.401) owned by a woman called Fat Toni. Franz takes to wearing a wig.
Days go by then with a great fuss Eva arrives with a newspaper with big front-page photos of Reinhold and Franz next to each other, both equally Wanted by police for Mieze’s murder!! Initially Fat Toni and Eva are horrified at the thought that Franz might actually have done it, but when he dissolves into helpless tears and sobbing they realise he didn’t.
It is autumn 1928. Franz wanders the streets in a stupor, devastated by Mieze’s murder. For obscure reasons he finds himself drawn back to the Tegel prison, then goes to the cemetery to see her grave, he hallucinates conversation with other dead people.
It is November (p.410). The Graf Zeppelin makes a low flight over Berlin, Weather conditions are given. Herbert is incensed at Mieze’s murder and scours Berlin to find Reinhold and take revenge. Franz slowly joins him. Franz takes a can of petrol to Reinhold’s house. The house speaks. the house has a conversation with Franz (pp.412-13), but Franz sets fire to it anyway, and it burns down.
Two angels, Terah and Sarug, follow Franz everywhere. They discuss his sad fate (pp.414-15). Eva calls Doctor Klemens to come assess Franz who is sunk into a deep depression, and recommends a break, a rest cure. Franz hangs round in bars. We meet other drinkers, overhear their conversations and even songs.
Hush-a-bye
Don’t you cry
When you wake
You’ll have a little cake.
As the text becomes evermore full of rhymes and jingles.
All his crying, all his protests, all his rage was idle prating,
Evidence was dead against him, and the chains for him were waiting. (p.421)
There is a big police raid on a bar in Rückerstrasse. I can’t make out whether it’s because the bar was a brothel or unlicensed or a criminal hangout or what, but some fifty cops in lots of cars raid it and round up all the customers who file out. All except for some guy who persists in sitting at his table sipping his beer. When several cops approach shouting at him to gt up and come along Franz (for it is indeed Franz Biberkopf) takes a revolver out of his pocket and shoots one. He falls but the other cops rush Franz, hitting his arm to make him drop the gun, beating him to the floor, he takes a rubber baton to the eye (p.430), and handcuffing him.
Some Tatsachenphantasie as Döblin quotes police arrest forms (Christian Name, Surname, Place of residence etc). Franz is brought in and taken to an office for interrogation.
Book nine (pages 435 to 478)
At the police station they quickly identify Franz as one of the two men wanted for the murder of Mieze. Meanwhile Reinhold, seeing the way things were going, uses the old crook’s method of getting arrested for a minor offence, using false papers. He mugs an old lady, is convicted with papers which identify him as Polish (a certain Moroskiewicz, p.435) and locked up in Brandenberg prison as a mugger, thus evading the death penalty for murder. Or so he thinks.
Threats come from two quarters. First, as luck would have it, there’s another petty criminal, Dluga, in the prison who knew the real Moroskiewicz and quickly susses out that Reinhold is neither Moroskiewicz nor a Pole. Reinhold has to bribe him with tobacco then accuses him of snitching, which gets him beaten up.
But worse is to come. Reinhold falls in love with a pretty boy, a petty criminal named Konrad, spends all his time billing and cooing with him. But Konrad is soon to be released, so Reinhold spends a last evening with him getting drunk on illicit alcohol and, oops, telling Konrad the whole story, about Franz and Mieze and burying her and his false name etc.
Konrad is soon released, looks up Reinhold’s most recent girlfriend, gets money out of her, meets another young lad and makes the mistake of boasting about his criminal mates inside, telling stories and before he knows it has told the full story about Reinhold, the murder, and his fake identity. The mate he’s told this swears to keep it a secret, but the next day goes to the police station and discovers the stuff about Reinhold is true and there’s a reward of 1,000 marks for anyone who turns him in. So he turns him in, tells the cops Reinhold is in Brandenberg prison under a false name. Cops investigate and arrest Reinhold, who is so beside himself with rage and frustration that they nearly take him to an asylum.
Meanwhile, Franz has gone into a catatonic trance so is taken by the cops to Buch Insane Asylum. He refuses to wear clothes, refuses to eat, loses weight, can be easily carried to the bath where he plays like a child. They force feed him through tubes but Franz vomits it all up.
Cut to a learned discussion between the physicians, with the young doctors enthusiastically prescribing either electro-shock therapy, or talking therapy copied from Freud in order to address the patient’s unresolved psychic conflicts.
As he loses weight his soul escapes his body, he has reached deeper strata of consciousness, his soul wants to be an animal or wind or seed blowing across the fields outside the asylum.
Franz hears Death singing (I couldn’t help thinking that Joyce’s epic ends on a wonderful note of life affirmation while this book, characteristically German, is obsessed with Death). Death tells Franz to start climbing the ladder towards him, illuminating the way with a barrage of hatchets which, as they fall and strike, let out light. Death lectures Franz, telling him that he insisted on being strong – after he was thrown under the car he resolved to rise again; when he had pretty little Mieze all he wanted to do was brag about her to Reinhold. He has insisted on being strong, seeing life on his terms and swanking, self-centred, instead of being meek and realising life is mixed.
Franz screams, screams all day and all night. But silently. To outward appearance he is catatonic and unmoving. Inside his head Death torments him with his stupidity and then a procession comes of all the crims he took up with, Lüders and Reinhold, why did I like them or hang out with them or try to impress them, Franz asks himself.
Ida appears before him, repeatedly buckling and bending, he asks her what is wrong, she turns and says ‘You are hitting me, Franz, you are killing me’, no no no no he cries. Mieze appears to him at noon, asking his forgiveness, Franz begs her to stay with him, but she can’t, she’s dead.
Crushed, Franz realises what a miserable worm he is. He sinks into a world of psychological pain, is burnt up, annihilated and, after much suffering, reborn.
Somehow his recovery is connected with a historic panorama of Napoleon’s army invading across the Rhine, of marching armies which have marched in the Russian Revolution, Napoleonic Wars, the Peasants Wars and so back into time, Death drawing his vast clock across the ravaged landscape and smiling, oh yes oh yes oh yes.
The old Franz Biberkopf is dead. A new man is reborn, call him Biberkopf. He starts talking. He answers all the police’s questions, though reluctantly. He doesn’t want to go back. But his alibis stand up and he is cleared of Mieze’s murder. And even (hard to believe) shooting a police officer appears to be only a cautionable offence. So after some weeks of slow physical and mental recovery, Biberkopf is released.
DEAR FATHERLAND, DON’T WORRY
I SHAN’T SLIP AGAIN IN A HURRY
Biberkopf returns to Berlin a changed man. Döblin gives us some Tatsachenphantasie, some facts and figures about Berlin’s train and subway and tram systems, about current building works and the latest advertising campaigns (‘Everybody admires the shoe / That’s brightly polished with Egu’).
Biberkopf meets up with Eva. Herbert’s been arrested by the cops and sent to prison for two years. Eva had been excited about carrying Franz’s baby but she had a miscarriage. Just as well. She is still supported by her sugardaddy ‘admirer’. They go out to visit Mieze’s grave and Eva is struck by how sober and sensible Franz is. Lays a wreath but then walks Eva across the road to a coffee shop where they enjoy some honey cake.
Franz is a witness at the trial of Reinhold. He tells all that he knows but isn’t malicious. He still has feelings of friendship for Reinhold. Reinhold, for his part, is puzzled by the new strange blank look on Biberkopf’s face. Reinhold is sentenced to ten years in prison.
Immediately afterwards Biberkopf is offered the job of doorman at a medium-sized factory. He has learned that one man alone is overwhelmed by fate. But a hundred or a thousand are stronger. The novel ends with military imagery, of drums rolling and soldiers marching, ‘we march to war with iron tread’.
It is a powerful image of determination and unity, of a mass of people united so that it’s difficult to tell whether it’s a communist or a fascist image, of people determined to look fate in the face, grab it, make it. And at the same time an odd way to end the novel.
Is that the most positive image Döblin can conceive, of free people marching to war with iron tread. Well, ten years later his people did march to war with iron tread and much good it did them.
I find reading these German books hard not because of their ‘experimental’ or ‘avant-garde’ ‘modernism’. As I’ve pointed out, above, all of Döblin’s techniques are child’s play compared with Joyce.
No, I found Berlin Alexanderplatz hard to read for the much more basic reasons that 1. I found the character’s behaviour at key moments and in general throughout the book, incomprehensible, and 2. I was deeply repelled by the characters’ casual violence in their thoughts and deeds.
1. Incomprehensibility
So I got to the end of the book and I still didn’t understand:
- the entire opening scene with Franz blundering into the home of some Jews who proceed to tell him a long-winded story about some Polish con artist (?)
- why Lüders going behind Franz’s back to threaten the skinny widow woman was so devastating to Franz (major plot crux 1)
- what the thinking was behind the scheme whereby Reinhold handed his discarded women over to Franz every month or so
- what made Reinhold suddenly snap and decide to chuck Franz out of the speeding getaway car (major plot crux 2)
- why Franz not only forgives Reinhold for trying to kill him, but ends up liking him and wanting to impress him
- the psychology whereby both Herbert and Franz were perfectly content to let their girlfriends (Eva and Mieze) go off and spend nights and weekends having sex with rich sugardaddies
- the psychology of Eva ‘finding’ young and beautiful Mieze ‘for’ Franz and making her his mistress while, at the same time, being hopelessly in love with Franz and wanting to have his baby
- why, in the end, Reinhold had to murder Mieze (major plot crux 3)
- why the devil Franz decides to start firing a revolver at the police during the raid of the club instead of going quietly?
So all the modernist techniques were easy and fun to process, but the basic psychology of the characters escaped me at almost every important turn of the plot.
2. Casual brutality
What horribly brutal people they are.
The reader searches high and low in vain for a touch of humour or gentleness. Kicking and stabbing, beating and raping appear to be the only way Germans can communicate with each other.
- Franz assaulted his wife violently enough to rupture her lung leading to her death.
- Walking through the Berlin streets, Franz fantasises about smashing all the shiny shop windows.
- On his first day out of prison, Franz rapes his wife’s sister, giving her a black eye in the process.
- Franz gets into a fight with commies at Hentchke’s pub.
- Franz enjoys watching his girlfriend fling the gay magazines at the newsvendor and yell at him in the street.
- When Meck tries to find out from Lüders where Franz has disappeared to, he doesn’t ask him firmly, he knocks him to the ground, beats him badly and threatens him with a knife.
- When Lüders goes to Franz’s flat, he keeps hold of an open knife in his pocket in case Franz turns nasty.
- In a casually brutal aside, Döblin makes a simile comparing Franz emerging into the slushy slippery Berlin streets, ‘just like an old horse that has slid on the wet pavement and gets a kick in the belly with a boot’ (p.164), yes that’s how Germans treat their animals
- The brutal way Pums’s gang treat Franz, even before they throw him out of the speeding car.
- The brutal way Reinhold beats his girlfriend’s face to a pulp without even thinking about it, permanently disfiguring her (p.228).
- The horrible way Franz beats Mieze when she tells him she’s in love with the young gentleman, knocking her to the floor and smashing her mouth.
- The horrible way Pums’s back gets burned during the bungled break-in at the factory and the rest of the gang laugh at him.
- The really horrible way Reinhold tries to rape and then murders Mieze.
Yuk.
I know the casual brutality reflects the working class and criminal characters Döblin has set out to depict but a) surely there were a few working class people who weren’t thieves and rapists b) surely even the roughest thugs have a few moments of charity and affection, c) Joyce was not only far more avant-garde and experimental in his form, but his selection of fairly ordinary characters to describe at such length are loveable and humane.
3. German humour
There are a few moments of comedy in this 480-page-long book, but a close examination suggests that German comedy doesn’t seem to be verbal, to involve wit or word play, puns or irony. It consists mostly in laughing at others’ misfortune or stupidity.
- Lūders laughs at Lina’s anxiety about Franz when the latter goes missing (p.118)
- Cilly humorously suggests to Franz a headline story in the newspaper such as, a paper-seller had to change some money and gave the right amount by mistake! (p, 208)
- Eva has a hysterical panic attack when she thinks Schreiber is about to pull a gun on Franz, leaping to her feet, screaming, making the two men themselves panic, knock over furniture, Schreiber hares off down the stairs, two men from the café come up to find out what one earth the noise is about, the landlady eventually comes in and throws a bucket of water over Eva to calm her down and now, finally calm and quiet, the soaking Eva softly says: ‘I want a roll’, and the two men from the café laugh (p. 246)
- Franz amuses a young woman named Emmi. When she asks where his other arm is, he says his girlfriend is so jealous, he leaves it back home with her as a pledge that he’ll return. And goes on to say he’s taught it tricks: it can stand on the table and give political speeches: ‘Only he who works shall eat!’ (p.258)
- Franz is joshing with some younger blokes down the pub. ‘As the Prussians used to say: hands on the seams of your trousers! And so say we, only not on your own!’ (p.261)
- Franz is in a getaway car with the Pums gang after pulling a job. The driver accidentally runs over a dog and is really upset. Reinhold and Franz roar with laughter at the bloke being so soft-headed. The man says: ‘A thing like that brings you bad luck’. Franz nudges the bloke next to him and says: ‘He means cats’ and everybody ‘roars with laughter’ (p.336)
- Reinhold pays Mieze a visit when Franz is out and flirts with her, rather intimidatingly. She asks him if he hasn’t got any work to do rather than lounging round with her. he replies: ‘Even the Lord sometimes takes a holiday, Fräulein, so we plain mortals should take at least two.’ She replies: ‘Well, I should say you’re taking three,’ and they both laugh (p.344)
- Reinhold keeps pestering Franz to tell him about his new girl (Mieze), saying it does no harm to describe her, does it? Franz admits, ‘No, it doesn’t harm me, Reinhold, but you’re such a swine,’ and they both laugh. (p.347)
- In a bar, three companions are drinking and joking. One says: An aviator walks onto a field, and there’s a girl sitting there. Says he: ‘Hey, Miss Lindbergh, how about some trick-flying together?’ Says she: ‘My name isn’t Lindbergh, It’s Fokker,’ and the three ‘roar with laughter’ (p.381)
- Some detectives come snooping the Alexander Quelle club. Two boys who’ve recently escaped from a reformatory are sitting chatting with the tinsmith. He has papers but they don’t, all three are ordered to the local police station where the boys immediately blab about what they’ve been up to. Ten the sops reveal they had no idea who they were and weren’t particularly looking for them. Damn, says the boys. ‘In that case we wouldn’t have told you how we hooked it’, and they all laugh together, boys and cops (p.385)
- The chief doctor in charge of Franz’s treatment in the mental institution listens to his two juniors squabbling about theories and ways to treat their catatonic patient, then gets up, laughs heartily and slaps their shoulders (p.450)
Setting them down like this I can appreciate that some of them are funny, I suppose. My negative perception is coloured by the often brutal or cruel remarks which jostle around them.
And in any case, old jokes are difficult to recapture even in English novels from the 1920s and 30s, let alone jokes in a foreign language, from the vanished world of 1920s Berlin.
And at least there is some humour in Alexanderplatz, unlike the solemn, philosophico-hysteria of the Hermann Broch trilogy I have just completed.
Summary
All that said, Berlin Alexanderplatz is a quite brilliant novel which gives you a vivid panoramic impression of 1920s Berlin and more insight into Germany and German-ness than anything else I’ve ever read.
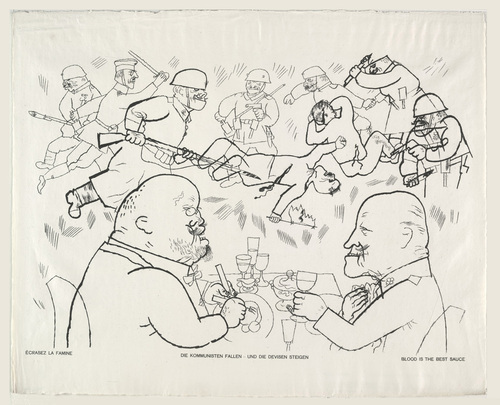
It is full of Weimar touches (the crippled war veterans, the legless man moving around on a wheeled trolley, the immense amount of prostitution, the pretty young things entertaining rich old sugardaddies, the casual sexual partners and the casual bisexuality of Reinhold, the threat of violence in the street from either the communists or the swastika-men, the hectic sense of things being continually hustled along without a chance to catch your breath given by the inclusion of so many newspaper headlines and events) which really do make it read like a verbal equivalent of harsh, unforgiving Weimar Republic artists like George Grosz and Otto Dix.

Twilight by George Grosz (1922)
Credit
Berlin Alexanderplatz was published in Germany in 1929. This translation by Eugene Jolas was published as Alexanderplatz by Martin Secker in 1931. All references are to the 1979 Penguin paperback edition.
Reviews of 20th century German literature
The Weimar Republic
German history