Laura Knight was the first woman to be elected to full membership of the Royal Academy of Arts (in 1936) and the first woman to receive a large retrospective exhibition at the Academy, in 1965. She was awarded a Damehood in 1929.
Born in 1877, Knight had a long life (passing away in 1970) and a long and successful career, working in oils, watercolours, etching, engraving and drypoint until well into the 1960s.
She never departed from the figurative, realist tradition of her youth and was, for this reason, in her heyday, one of the most popular painters in Britain.

Portrait of Joan Rhodes by Laura Knight (1955) © The estate of Dame Laura Knight. Photo credit: Royal Academy of Arts
Given Knight’s mid-century fame, and her role as a pioneering woman artist, it is a little surprising that this FREE display of some of her work is a) so small and b) tucked away in a dingy room through a doorway off of the main first floor landing. There was no signage, I had to ask an RA staffer where it was hidden.
If you google Knight or look at her Wikipedia article, you immediately see a series of highly realistic and vivid oil paintings, starting with the cracking Self Portrait with Nude of 1913, and including the evocative paintings she did during the Second World War (she became an official war artist at the outbreak of war, and her portrait of Ruby Loftus operating industrial machinery was picture of the year at the Academy’s 1943 summer exhibition).
As you explore further online you come across lots and lots of oil paintings of chocolate box scenes of the countryside, especially of the Cornish coast, featuring soulful looking ladies with parasols (before the First War) or in flapper style dresses and chapeaux (after the First War).
In this little display there are only three oil paintings on display here, although they include the very striking portrait of Joan Rhodes (above) and an equally realistic and sensual double nude, Dawn. (It is hard not to be struck by the firm pink bosoms in this painting, though maybe I am meant to be paying attention to the women’s soulful gazes…)
No, the bulk of this display is made up of display cases of Knight’s drawings and sketchbooks of which the Academy holds a substantial collection – small, monochrome, often unfinished sketches, which are – to be frank – of variable quality and finish, some were very appealing, some seemed, well, a bit scrappy.
The works are grouped into three distinct themes from Knight’s long working life – the countryside, the nude and scenes from the theatre, ballet and circus.
Countryside
Knight had several spells of living in the countryside – in the 1890s she moved to the Yorkshire fishing village of Staithes and painted scenes of the coast and life among the fishermen and their wives. In 1907 Knight and her husband moved to Cornwall and became central figures in the artists’ colony known as the Newlyn School. In the 1930s she and her husband settled in the Malvern Hills, where she remained for the rest of her life.
Thus the exhibition includes sketches she did of Mousehole in Cornwall, alongside sketches of a ploughed field, trees beside a river, Richmond Park, Bodmin Moor, two land girls in a field, seeding potatoes, and so on.

Mousehole Harbour, Cornwall, with Figures in Foreground by Laura Knight (mid-1920s or early 1930s) © The Estate of Dame Laura Knight
It was only later, when I googled her many finished paintings of Mousehole and other Cornish scenes that I realised where these sketches were heading, and what I was missing. I wish the exhibition had included at least one finished painting of this kind of scene alongside the sketches, to help you understand the process better, and the purpose of the sketches.
Nudes
We’ve already met the two dramatic nude women in Dawn. There are a small number of other nude sketches and studies on display, which I thought were a bit so-so. Like the countryside sketches, they strongly suggest that the ‘magic’ of Knight’s paintings was precisely in the painting, in her skill at creating an airy, light and luminous finish with oil paints.
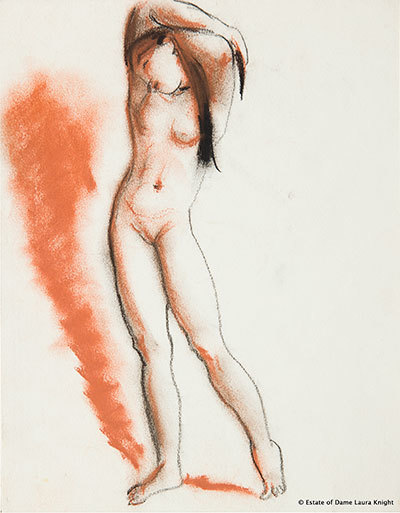
Standing Nude with Her Arms Behind her Head by Laura Knight (mid-1950s) © The Estate of Dame Laura Knight
Theatre, ballet and circus
This broad subject area contains the largest number of sketches and drawings. Knight sketched ballet dancers, and circus performers, there are drawings of boxing matches held among soldiers training during World War One, and ice skaters and trapeze artists and many other performers. The wall labels tell us that she even spent some months travelling with famous circuses of the Edwardian era, drawing and sketching every day.
They’re all competent. Some of them piqued my interest. But none of them seemed to me as vivid as the drawings of, say Edward Ardizzone, who had a comparable sketching style, using multitudes of loosely drawn lines to build up form and composition.
Maybe I’m mixing up fine art (Knight) with book illustration (Ardizzone) and maybe I’m giving away my failings of taste in saying so, but I much prefer the Ardizzone. It’s more vivid, more evocative, more physically pleasing (more tactile), more fun.
Also, as with the nudes and landscapes, a quick search online reveals that Knight converted her sketches into scores and scores of paintings of the circus, and I immediately found the paintings much more pleasurable than the sketches – a little cheesy and old-fashioned, like vintage Christmas cards, but much more finished and complete than the sketches.
Grievance
The introductory panel and all the wall labels exude what you could call the standard feminist spirit of grievance and offence. There’s a long list of offences to absorb.
The curators point out that Knight, despite her success with the public, was only granted membership of the Royal Academy in 1936! That she was the first woman to achieve this accolade (why so late Royal Academy)! But that, even then, she wasn’t invited to Academicians’ Annual Dinner until 1967!
We are told that, as a woman art student before the Great War, she was forbidden to paint or sketch from real naked models but had to work from sculptures and statues! It was only in the 1930s, in Newlyn, that she was able local people to pose nude for her! And so a work like Dawn can be seen as an act of defiance against a male-dominated art world!
I’m sure all of this, and much more along the same lines, is true and scandalous and we should all be outraged by it. But, seen from another perspective, all this righteous indignation amounts to a skilful evasion of the rather obvious question, which is whether Knight’s art is any good – or is of anything of other than antiquarian interest, dusted off and used as a pretext for the righteous anger of modern curators?
This tricky question is not addressed anywhere in the (very informative) wall labels, but, when you think about it, is amply answered by:
- The Academy’s choice of location for this little ‘exhibition’ – tucked away in a dark and dingy side-room.
- The fact that it is more of a ‘display’ of half a dozen notebooks, three paintings and a poster, than a full-blooded exhibition. An after-thought.
If Laura Knight is so eminent and so worthy of consideration, why didn’t the Academy give her a larger exhibition in a more prominent space?
Ironically, the curators who complain that Knight was overlooked and patronised in her own time, have done quite a good job of repeating the gesture – of displaying only a small and not very persuasive part of her output, in a hidden-away side room which nobody in a hurry to see the blockbuster shows on Anthony Gormley or Helena Schjerfbeck or Félix Vallotton is in too much danger of stumbling across.
Suggestion
In all seriousness, why not give Laura Knight a much bigger exhibition? If you look at the paintings embedded in the Wikipedia article or all across Google, it’s clear that she painted absolutely brilliantly, but in a straightforward naturalistic style which was completely outdated and provincial by the 1930s, let alone the 40s or 50s – in a style which carried on its Edwardian naturalism into the atomic age as if the rest of modern art had never existed.
But despite that – or more likely, because of it – Knight was very popular and successful with the public. Her paintings of Edwardian children playing on the beach or soulful ladies standing on clifftops sold by the dozen and – from a Google search of them – look immensely pleasing and reassuring in a lovely, airy, chocolate-box kind of way. And her wartime paintings perfectly capture the earnest heroism of the conflict, and of the social realism, the committedness, of the wartime artists.
To me this all suggests a whole area of investigation, an enquiry into why British artistic taste remained so isolated and uncosmopolitan for so long, which would reference:
- the way the director of Tate in the 1930s could proudly say that Tate would only buy work by the young whippersnapper Henry Moore ‘over his dead body’
- or Sir Alfred Munnings, the horse-painting president of the Royal Academy, addressing the academy’s 1949 annual banquet, delivered a drunken rant against all modern art, and invoked the support of Winston Churchill (sitting next to him) who he claimed, had once asked him: ‘Alfred, if you met Picasso coming down the street would you join me in kicking his … something, something?’ ‘And I said ‘Yes, sir! Yes I would!’
A big exhibition of Knight’s work would:
- put to the test the curators’ claims about her importance and relevance
- be very popular among the sizeable audience, who still like their art extremely traditional (think of the sales of prints and other merchandise!)
- allow the curators to explore and analyse the long-lasting appeal and influence of the anti-continental, anti-modernist, anti-avant-garde tradition in 20th century English art of which, for all her skill and ability, Laura Knight appears to have been a leading example
This – the philistinism of English art, the determined rejection of all 20th century, contemporary and modern trends in art and literature in preference for the tried and tested and traditional – is something you rarely hear discussed or explained, maybe because it’s too big a subject, or too vague a subject, or too shameful a subject. But it’s something I’d love someone better educated and more knowledgeable in art history to explain to me. And I’d really enjoy seeing more of Laura Knight’s lovely airy innocent paintings in the flesh. Why not combine the two?
For once mount an exhibition which is not about a pioneer or explorer or breaker of new ground, but about a highly capable painter of extremely traditional and patriotic and reassuring paintings, and explain how and why the taste which informed her and her audience remained so institutionally and economically and culturally powerful in Britain for so long.
Related links
- Laura Knight continues at the Royal Academy until 2 February 2020
- Laura Knight website






















